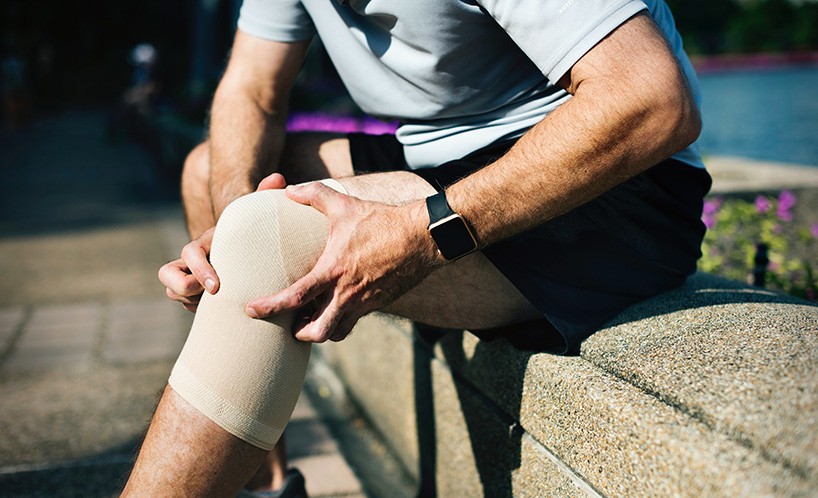
In most cases, personal injury includes physical damage to the body, and pain is a common component. Chronic pain is especially significant, because it may affect one’s ability to perform daily activities. In addition, limb loss and other catastrophic injuries can cause significant pain and suffering for victims. It is difficult to quantify the extent of such damage and suffering, but it is common to obtain compensation for it. It is important to note, however, that pain and suffering do not have to be immediate or severe. If you are suffering due to someone else’s negligence, visit dozierlaw.com/attorneys/personal-injury-attorneys-savannah.
In many cases, pain and suffering are calculated by using the multiplier method. Under this method, the total economic damages are multiplied by a number, depending on the severity of the injury. The multiplier is usually one to five. The per-diem method, on the other hand, assigns a dollar amount to each day from the date of the accident to the date when the plaintiff is expected to recover to a maximum level.
The term pain and suffering can be difficult to quantify, but it can represent a large portion of a personal injury claimant’s total losses. Pain and suffering are generally defined as emotional and physical suffering, including sleeplessness, anxiety, and loss of consortium. It is important to note, however, that pain and suffering damages can also apply to wrongful death claims. A wrongful death case can also include pain and suffering, as well as lost wages and household services.
The value of pain and suffering can differ from case to case, but there are general guidelines. Pain and suffering damages include physical, mental, and emotional effects and are estimated to last a lifetime. Pain and suffering damages are recoverable when the insurance company agrees to pay you for the pain and suffering you’ve experienced as a result of the injury. The more evidence you provide, the higher your chances of recovering a satisfactory compensation.